目录
本文主要参考《JavaScript数据结构与算法第三版》一书, 系统学习梳理JavaScript数据结构(栈、队列、链表、集合、字典、散列表、二叉搜索树、堆、图)及与数据结构相关的算法
栈
栈的简易实现
tsclass Stack<T = any> {
// 这里为了leetcode调试方便暂不使用es6私有属性
// #size = 0;
_size = 0;
get size() {
return this._size;
}
set size(val: number) {
this._size = val;
}
// accessor size = 0; 私有属性的简写形式 // 候选阶段,还不能使用
_items: { [key: number]: T } = Object.create(null);
get isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
constructor() {}
push(element: T) {
this._items[this.size] = element;
this.size++;
}
pop(): T | undefined {
if (this.isEmpty) return;
const result = this._items[--this._size];
delete this._items[this._size];
return result;
}
peek(): T | undefined {
if (this.isEmpty) return;
return this._items[this._size - 1];
}
clear() {
this._items = Object.create(null);
this._size = 0;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty) {
return '';
}
let str = `${this._items[0]}`;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size; i++) {
str += `, ${this._items[i]}`;
}
return str;
}
}
栈的用途
- 10进制转2进制

- v8 JS调用栈
- leetcode算法题
- 20. 有效的括号
-
- 最长有效括号
队列
栈是后进先出, 队列是先进先出, 双端队列可以类比数组了两头都可以进和出。
tsclass Queue<T = any> {
#count = 0;
#lowest = 0;
#items: { [key: number]: T } = Object.create(null);
get isEmpty() {
return this.#count === this.#lowest;
}
get size() {
return this.#count - this.#lowest;
}
enqueue(element: T) {
this.#items[++this.#count] = element;
}
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty) return;
const result = this.#items[this.#lowest + 1];
this.#lowest++;
return result;
}
peek(): T | undefined {
if (this.isEmpty) return;
return this.#items[this.#lowest + 1];
}
clear() {
this.#count = 0;
this.#lowest = 0;
this.#items = Object.create({});
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty) {
return '';
}
let str = `${this.#items[this.#lowest + 1]}`;
for (let i = this.#lowest + 2; i <= this.#count; i++) {
str += `, ${this.#items[i]}`;
}
return str;
}
}
双端队列
ts// class Deque extends Queue
// 由于私有属性不能继承, 这里写一下抽象代码
class Deque<T> {
addFront(element: T): void {}
addBack(element: T): void {}
removeFront(): void {}
removeBack(): void {}
peekFront(): T {}
peekBack(): T {}
}
队列的用途
链表
JavaScript数组非常灵活,但数组的缺点是中间节点的删除或修改成本很高,因为需要移动元素。
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中,并不是连续放置的。 每一个元素有存储元素本身的节点和指向下一个元素的引用组成。

单向链表
tsexport class MyNode<T = any> {
public next: null | MyNode<T> = null;
constructor(public element: T) {}
}
export class LinkedList<T = any> {
public head: null | MyNode<T> = null;
public count = 0;
constructor(public equalsFn = (a: T, b: T) => a === b) {}
push(element: T) {
const node = new MyNode(element);
let current: undefined | MyNode<T>;
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = new MyNode(element);
}
++this.count;
}
getElementAt(index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index && node != null; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return null;
}
insert(element: T, index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new MyNode(element);
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head;
node.next = current || null;
this.head = node;
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)!;
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current!.next || null;
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)!;
current = prev.next!;
prev.next = current!.next;
}
this.count--;
return current!.element;
}
return undefined;
}
indexOf(element: T) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
if (this.equalsFn(element, current.element)) {
return i;
}
current = current.next || null;
}
return -1;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
clear() {
this.head = null;
this.count = 0;
}
toString() {
if (this.head == null) {
return '';
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
}
环状链表、排序链表
tsexport class CircularLinkedList<T = any> extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
}
insert(element: T, index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new MyNode(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size())!;
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
// 这种场景没有变化
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)!;
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head!;
if (index === 0) {
// 需要维护环结构
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = null;
} else {
const removed = this.head!;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size())!;
this.head = this.head!.next;
current.next = this.head;
current = removed;
}
} else {
// 不需要维护环结构
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)!;
prev.next = prev.next!.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
}
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THEN: 1,
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return 0;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THEN;
}
export class SortedListList<T = any> extends LinkedList {
constructor(
public equalsFn = (a: T, b: T) => a === b,
public compareFn = defaultCompare
) {
super(equalsFn);
}
insert(element: T, index = 0) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return super.insert(element, index);
}
const pos = this.getIndexNextSortedElement(element);
return super.insert(element, pos);
}
getIndexNextSortedElement(element: T): number {
let current = this.head!;
let i = 0;
for (; i < this.size(); i++) {
const comp = this.compareFn(element, current.element);
if (comp === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return i;
}
current = current.next!;
}
return i;
}
}
双向链表
tsexport class LinkNode<T = any> {
public next: LinkNode<T> | null = null;
public prev: LinkNode<T> | null = null;
constructor(public value: T) {
this.value = value;
}
toString() {
return `Node(${this.value})`;
}
}
export class DoubleLinkList<T = any> {
public get size() {
return this.#size;
}
#size = 0;
private head: LinkNode<T> | null = null;
private tail: LinkNode<T> | null = null;
private init(element: T) {
this.tail = this.head = new LinkNode(element);
this.head.next = null;
this.head.prev = null;
this.#size = 1;
}
append(element: T) {
if (this.tail === null) {
this.init(element);
return;
}
const node = new LinkNode(element);
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = this.tail.next;
this.tail.next = null;
this.#size += 1;
}
appendFront(element: T) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.init(element);
return;
}
const node = new LinkNode(element);
this.head.prev = node;
node.next = this.head;
this.head = this.head.prev;
this.#size += 1;
}
remove(element: T | null = null) {
// 链表是空
if (this.head === null) {
return null;
}
// 默认删除最后一个
let node: LinkNode<T>;
if (element === null) {
node = this.tail!;
} else {
node = this.findNode(element);
}
// 只有一个节点 移除
if (this.head === this.tail) {
if (this.head.value === node.value) {
this.head = this.tail = null;
this.#size = 0;
return node;
}
return null;
}
if (node === this.head) {
return this.unshift();
}
if (node === this.tail) {
return this.pop();
}
// 移除中间节点
node.next!.prev = node.prev;
node.prev!.next = node.next;
this.#size -= 1;
return node;
}
findNode(element: T): LinkNode<T> {
let current = this.head!;
while (current.next) {
if (element === current.value) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
}
throw new Error(); //
}
unshift() {
// 没有元素
if (this.head === null) return null;
// 只有一个元素 或 没有元素
const node = this.head;
if (this.tail === this.head) {
this.head = this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next!;
this.head.prev = null;
}
this.#size -= 1;
return node;
}
pop() {
// 没有元素
if (this.tail === null) return null;
const node = this.tail;
// 只有一个元素
if (this.tail === this.head!) {
this.head = this.tail = null;
} else {
this.tail = this.tail.prev!;
this.tail.next = null;
}
this.#size -= 1;
return node;
}
toString() {
const result: string[] = [];
let start = this.head;
while (start) {
result.push(start.toString());
start = start.next;
}
return result.join(' <==> ');
}
}
链表用途
- 判断一个链表是否有环
- 设置两个变量 一个跑1步,一个跑两步,如果两者相等则存在环
- 移除链表倒说第N个元素
- 设置两个变量 一个先跑N步,当先跑的到头, 则另一个变量就是需要操作的
- leetcode 19
- leetcode
- leetcode 2. 两数之和
- leetcode 21. 合并两个有序链表
- leetcode 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
- leetcode 25. K 个一组翻转链表
- 通过链表实现栈
tsimport { DoubleLinkList } from './doubleLinkedList';
export class StackLinkedList<T> {
public items = new DoubleLinkList<T>();
constructor() {}
push(element: T) {
this.items.append(element);
}
pop() {
if (this.items.size) {
return undefined;
}
return this.items.remove();
}
}
- ReactJS使用了大量的链表 effectList
- 缓存算法 LFU (高速缓存的替换策略、虚拟内存替换算法)
- Linux内存管理 Buddy内存交换算法
集合
集合是由一组无序且唯一(即不能重复)的项组成。
JavaScript 提供了Set类
- add()
- delete()
- has()
- clear()
- size
- values()
集合的运算 交叉并补
字典
字典和集合很类似,集合以【值、值】的形式储存元素,字典以【键、值】的形式存储元素,字典也称作映射、符号表或关联数组
与Set类似,JavaScript提供了Map类
散列表
散列表也称作HashMap、HashTable
散列算法的作用是尽可能快地在数据结构中找到一个值。在之前的数据结构中获得一个值 (使用get方法),需要迭代整个数据结构来找到它。如果使用散列函数,就知道值的具体位置,因此能够快速检索到该值。 散列函数的作用是给定一个键值, 然后返回值在表中的地址。
散列表有一些在计算机科学中应用的例子。因为它是字典的一种实现,所以可以用作关联数组。它也可以用来对数据库进行索引。当我们在关系型数据库(如MySQL、Microsoft SQL Server、Oracle,等等)中创建一个新的表时,一个不错的做法是同时创建一个索引来 更快地查询到记录的key。在这种情况下,散列表可以用来保存键和对表中记录的引用。另一个很常见的应用是使用散列表来表示对象。JavaScript语言内部就是使用散列表来表示每个对象。此时,对象的每个属性和方法(成员)被存储为key对象类型,每个key指向对应的对象成员。
在散列表中hash可能存在冲突问题, 可以通过分离链表、线性探查、双散列表的方式解决冲突
- 分离链表

- 线性探查
线性探查技术有两种方式
- 软删除,随着操作的进行,散列表的效率会降低
- 删除后移动位置, 虽然优化了查找效率,但添加时候增加的工作量
JavaScript数组会动态扩容。
创建性能更好的散列函数要考虑的因素
- 插入和检索的时间
- 较低的冲突
比lose lose更好的散列函数是djb2
- 双散列表
如果存在hash冲突就继续使用散列算法
WeakMap 弱引用、key只能是对象、不提供遍历方法
树
- 数组插入节点开销比较大;链表插入节点降低了开销,但增加了查找的开销。有没有折中的方案,插入小于数组开销查找小于链表开销? 这就用到了二叉树搜索树
- 二叉树: 树中的节点组多有两个
- 二叉搜索树BST: 二叉树的一种,左边只能存储比父节点小的元素,右边存储比节点大的元素。
二叉搜索树示例代码, 测试用例
tsexport class TreeNode<T = any> {
public left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
public right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
constructor(public key: T) {}
}
export class BinarySearchTree<T = any> {
public root: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
constructor(public compareFn = (a, b) => a - b) {
this.root = null;
}
insert(key: T): void {
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = new TreeNode(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root!, key);
}
}
insertNode(node: TreeNode, key: T) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) > 0) {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = new TreeNode(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
} else {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = new TreeNode(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
}
}
search(key: T, node = this.root): boolean {
if (!node) return false;
let current = node;
const diff = this.compareFn(key, current.key);
if (diff === 0) {
return true;
}
const currentNode = diff > 0 ? current.right : current.left;
return this.search(key, currentNode!);
}
min(): TreeNode<T> {
if (this.root == null) throw new Error();
let current = this.root;
while (current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
max(): TreeNode<T> {
if (this.root == null) throw new Error();
let current = this.root;
while (current.right) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
remove(key: T) {
this.removeNode(this.root, key, null, 'left');
}
removeNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, key: T, parent: TreeNode<T> | null, dir: 'left' | 'right' = 'left'): TreeNode<T> | null {
if(!node) return null;
const flag = this.compareFn(node.key, key);
if(flag === 0) {
if(!parent) {
this.root = null;
return node;
} else {
if(!node.left && !node.right) {
parent[dir] = null;
} else if(!node.left) {
parent[dir] = node.right;
} else {
parent[dir] = node.left;
}
return node;
}
} else if (flag > 0) {
return this.removeNode(node.right, key, node);
} else {
return this.removeNode(node.left, key, node);
}
}
minNode(node: TreeNode<T>): TreeNode<T> {
let current = node;
while (current.left) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
// 先序遍历 打印结构化文档
preOrderTraverse(callback: Function): void {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
// 中序遍历 从小到大排序
inOrderTraverse(callback: Function): void {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
// 后序遍历 统计文件夹大小
postOrderTraverse(callback: Function): void {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, callback: Function) {
if (node !== null) {
callback(node.key);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, callback: Function) {
if (node !== null) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, callback: Function) {
if (node !== null) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.key);
}
}
}
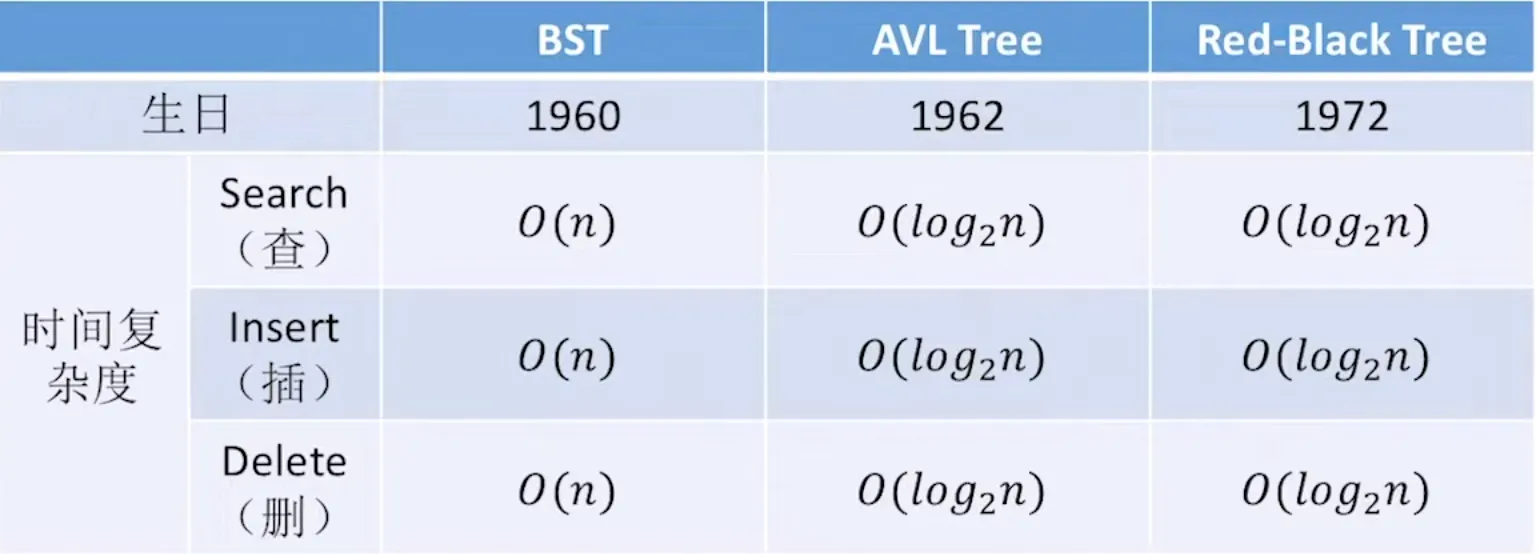
如果不对二叉搜索树进行维护,极端情况二叉搜索树会蜕变成链表结构,查找效率蜕变为。这就用到了AVL自平衡树。
AVL树
AVL树是一种BST,在插入元素或者删除元素需要维护树的平衡,任何一个节点左子树和右子树的高度最多差1。
AVLTree可以继承BST,覆盖insert、insertNode和removeNode方法,其他的BST方法都会被AVLTree继承
有四种场景
- LL 向右单旋转 比如依次插入
[3,2,1] - RR 向左单旋转 比如一次插入
[1,2,3] - LR 向右双旋转 (先LL旋转,在RR旋转) 比如往
<这种结构插入叶子结点, 先LL变成 结构1,然后 LL旋转
- RL 向左双旋转 (先RR旋转,在LL旋转)比如往
>这种结构插入叶子结点, 先LL变成 结构1,然后 LL旋转
AVL树的简易实现
tsimport { BinarySearchTree, TreeNode } from './binarySearchTree';
enum BalanceFactor {
UNBALANCED_RIGHT = -2,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT = -1,
BALANCED = 0,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT = 1,
UNBALANCED_LEFT = 2,
}
export default class AVLTree<T = any> extends BinarySearchTree {
constructor(public compareFn = (a, b) => a - b) {
super(compareFn);
this.root = null;
}
getNodeHeight(node: TreeNode<T> | null = null) {
if (node === null) {
return -1;
}
return (
Math.max(this.getNodeHeight(node.left), this.getNodeHeight(node.right)) +
1
);
}
getBalanceFactor(node: TreeNode<T>) {
const heightDifference: BalanceFactor =
this.getNodeHeight(node.left) - this.getNodeHeight(node.right);
return heightDifference;
}
// 向右单旋转
// 该node的Height为+2 要插入的数字是1
rotationLL(node: TreeNode<T>) {
// 3
// 2 => 2
// 1 1 3
const tmp = node.left!; // 2
node.left = tmp.right; // 2.5
tmp.right = node; // 3
return tmp; // 2
}
// 向左单旋转
// 该node的Height为-2 要插入的数字是3
rotationRR(node: TreeNode<T>) {
// 1
// 2 => 2
// 3 1 3
const tmp = node.right!; // 2
node.right = tmp.left; // 1.5
tmp.left = node; // 1
return tmp;
}
// 向右双旋转 感觉应该叫 向左旋转+向右旋转才对 ??
// 该node的Height为2 要插入的数字是 2
rotationLR(node: TreeNode<T>) {
// 3 3 2
// 1 c4 rotateLeft=> 2 c4 rotateRight=> 1 3
// c1 2 1 c3 c1 c2 c3 c4
// c1 c3 c1 c2
node.left = this.rotationRR(node.left!);
return this.rotationLL(node);
}
// 向左双旋转
// 该node的Height为-2 要插入的数字是 2
rotationRL(node: TreeNode<T>) {
// 1 1 2
// c1 3 rotateRight=> c1 2 rotateLeft=> 1 3
// 2 c4 c2 3 c1 c2 c3 c4
// c2 c3 c3 c4
node.right = this.rotationLL(node.right!);
return this.rotationRR(node);
}
insert(key: T) {
this.root = this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
insertNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, key: T): TreeNode<T> {
// 插入同BST
if (node == null) {
return new TreeNode(key);
} else if (this.compareFN(key, node.key) < 0) {
node.left = this.insertNode(node.left, key);
} else if (this.compareFN(key, node.key) > 0) {
node.right = this.insertNode(node.right, key);
} else {
return node; // 重复的键
}
// 如果需要对树进行平衡操作
const balanceFactor = this.getBalanceFactor(node);
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
if (this.compareFN(key, node.left!.key) < 0) {
node = this.rotationLL(node);
} else {
return this.rotationLR(node);
}
}
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.right!.key) > 0) {
node = this.rotationRR(node);
} else {
return this.rotationRL(node);
}
}
return node;
}
removeNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, key: T) {
node = super.removeNode(node, key);
if (node === null) return null;
// 检查树是否平衡
const balanceFactor = this.getBalanceFactor(node);
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
const balanceFactorLeft = this.getBalanceFactor(node.left!);
if (
balanceFactorLeft === BalanceFactor.BALANCED ||
balanceFactorLeft === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT
) {
return this.rotationLL(node);
}
if (balanceFactorLeft === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
return this.rotationLR(node.left!);
}
}
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
const balanceFactorRight = this.getBalanceFactor(node.right!);
if (
balanceFactorRight === BalanceFactor.BALANCED ||
balanceFactorRight === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT
) {
return this.rotationRR(node);
}
if (balanceFactorRight === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
return this.rotationRL(node.right!);
}
}
return node;
}
}
如何知道二叉树的结构呢?
给每一个节点标记权重,叶子结点权重为0, 非叶子节点的权重等与左子节点路径长度减去右子节点路径长度

所以新插入节点要往上更新权重,如果跟节点权重为+2 或 -2则需要平衡
红黑树
对于搜索很频繁、插入删除很少的场景AVL树的应用场景,但对于插入删除频繁,查询很少的场景就要使用红黑树了。
红黑树的规则
- 每个节点不是红的就是黑的
- 树的根节点是黑的
- 所有叶子结点都是黑的(用Null引用表示的结点)
- 如果一个节点是红的,则它的两个字节点都是黑的,
- 不能出现连续红,可以出现连续黑,
- 从给定节点到它的后代节点,所有路径包含相同的黑节点
插入节点
- 先查找,确定插入的位置
- 如果新节点是根 -- 染为黑色
- 新节点非根 -- 染为红色
- 新插入的节点满足红黑树定义 则插入结束
- 不满足红黑树定义则需要调整
- 黑叔 旋转+染色 旋转规则同AVL
- LL型 父换爷 + 染色
- RR型 父换爷 + 染色
- LR型 子换爷 + 染色
- RL型 子换爷 + 染色
- 红叔 染色+变新 染色规则看叔叔的脸色
- 叔父爷染色,爷变为新节点

红黑树的简易实现
tsimport { BinarySearchTree, TreeNode } from './binarySearchTree';
/**
* 对于搜索频次很少,插入删除频繁的场景使用红黑树
* 红黑树的规则
* 1. 根叶黑
* 2. 左根右
* 3. 不红红
* 4. 黑路通
*/
enum Colors {
RED = 'RED',
BLACK = 'BLACK',
}
export class RedBlackNode<T = any> extends TreeNode {
public parent: RedBlackNode<T> | null = null;
public left: RedBlackNode<T> | null = null;
public right: RedBlackNode<T> | null = null;
constructor(
public key: T,
public color = Colors.BLACK
) {
super(key);
}
isRED() {
return this.color === Colors.RED;
}
}
export class RedBlackTree<T = any> extends BinarySearchTree {
root: (RedBlackNode<T> & {}) | null = null;
constructor(public compareFn = (a, b) => a - b) {
super(compareFn);
this.root = null;
}
insert(key: T) {
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = new RedBlackNode(key);
this.root.color = Colors.BLACK;
} else {
const newNode = this.insertNode(this.root, key);
this.fixTreeProperties(newNode);
}
}
insertNode(node: RedBlackNode<T>, key: T): RedBlackNode<T> | null {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) < 0) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = new RedBlackNode(key, Colors.RED);
node.left.parent = node;
return node.left;
} else {
return this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
} else {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = new RedBlackNode(key, Colors.RED);
node.right.parent = node;
return node.right;
} else {
return this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
}
fixTreeProperties(node: RedBlackNode<T> | null) {
// 是否破坏 不红红 原则
while (node?.parent?.isRED() && node.color !== Colors.BLACK) {
let parent = node.parent;
const grandParent = parent.parent;
// A 父节点是左侧子节点
if (grandParent && grandParent.left === parent) {
const uncle = grandParent.right;
// 叔节点也是红色--只需要重新染色
if (uncle && uncle.color === Colors.RED) {
grandParent.color = Colors.RED;
parent.color = Colors.BLACK;
uncle.color = Colors.BLACK;
node = grandParent; // 将爷节点视为新插入的节点
} else {
// 2A 节点是右侧子节点--左旋转
if (parent.right === node) {
// LR型
this.rotationRR(parent);
this.rotationLL(grandParent);
// 染色 儿和爷节点
node.color = Colors.BLACK;
node.right!.color = Colors.RED;
} else {
// 3A 节点是左侧子节点--右旋转
// 黑叔 右单旋父换爷 染色
this.rotationLL(grandParent);
node.parent!.color = Colors.BLACK;
node.parent!.right!.color = Colors.RED;
}
}
} else {
// B父节点是右侧子节点 插入30
//叔父爷同时变色
const uncle = grandParent!.left;
if (uncle && uncle.color === Colors.RED) {
grandParent!.color = Colors.RED;
parent.color = Colors.BLACK;
uncle.color = Colors.BLACK;
node = grandParent;
} else {
// 2B 节点是左侧子节点--右旋转
if (parent.left === node) {
this.rotationLL(parent);
this.rotationRR(grandParent!);
// 染色 儿和爷节点 todo check
node.color = Colors.BLACK;
node.left!.color = Colors.RED;
} else {
// 3B 节点是右侧子节点--左旋转
this.rotationRR(grandParent!);
node.parent.color = Colors.BLACK;
node.parent.left!.color = Colors.RED;
}
}
}
}
this.root!.color = Colors.BLACK;
}
rotationLL(node: RedBlackNode<T>): RedBlackNode<T> {
const tmp = node.left!;
node.left = tmp.right;
if (tmp.right && tmp.right.key) {
tmp.right.parent = node;
}
tmp.parent = node.parent;
if (!node.parent) {
this.root = tmp;
} else {
if (node === node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = tmp;
} else {
node.parent.right = tmp;
}
}
tmp.right = node;
node.parent = tmp;
return tmp;
}
rotationRR(node: RedBlackNode<T>): RedBlackNode<T> {
const tmp = node.right!;
node.right = tmp.left;
if (tmp.left?.key) {
tmp.left.parent = node;
}
tmp.parent = node.parent;
if (!node.parent) {
this.root = tmp;
} else {
if (node === node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = tmp;
} else {
node.parent.right = tmp;
}
}
tmp.left = node;
node.parent = tmp;
return tmp;
}
// todo removeNode
}
参考资料: 红黑树的插入
Huffman树
HuffmanTree翻译成中文是赫夫曼树,也叫哈夫曼树,还叫霍夫曼树。
它的定义是:
给定n个权值作为n的叶子结点,构造一颗二叉树,使得该树的WPL(带权路径长度)达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树。
赫夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的节点离根较近。
赫夫曼树的一些概念
- 路径和路径长度:在一颗树中从一个节点往下,可以达到孩子节点或孙子节点之间的通路,成为路径。通路中分支的路径数目称之为路径的长度,若规定跟节点的层数为1,则从跟节点到第L层节点的路径长度为L-1
- 节点的权: 若树中的节点赋给一个某种有含义的树枝,则这个数值就是节点的权。
- 带权路径长度: 节点的权值 * (节点所在的层L-1),
举个例子,下图中间的树wpl最小,才是 HuffmanTree

注意:权重最小的树可能有多个, 如上图3与7交换位置,wpl不变,都是赫夫曼树。
那么赫夫曼树有什么用呢? 它是文件无损压缩的原理! 我们先来用代码实现一下,再解释文件压缩的原理。
给定一个数列{13, 7, 8, 3, 29, 6 1}, 要求转为一个HuffmanTree
思路分析:
- 从小到大排序,每一个数据都是一个节点,每一个节点可以看成是一个最简单的二叉树。
- 取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树,
- 组成一个新的二叉树,该新的二叉树根节点的权值是前面两个二叉树根节点权值之和
- 再将这颗新的二叉树,以跟节点权值大小再次排序,不断重复1,2,3,4的步骤,直到数列中所有的数据都被处理,就得到一颗
HuffmanTree。
代码实现
tsexport class TreeNode<T> {
/**
* char目前用不到,文件压缩的时候会用到
* null表示非叶子节点
*/
public char: string | null = null;
public left: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
public right: TreeNode<T> | null = null;
constructor(public key: T | null = null) {}
}
export function createHuffmanTree(arr: number[]) {
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const trees: TreeNode<number>[] = arr.map((it) => new TreeNode(it));
while (trees.length > 1) {
const leftNode = trees.shift()!;
const rightNode = trees.shift()!;
const parentNode = new TreeNode(leftNode.key! + rightNode.key!);
parentNode.left = leftNode;
parentNode.right = rightNode;
binaryInsert(trees, parentNode);
}
return trees[0];
function binaryInsert(
trees: TreeNode<number>[],
tree: TreeNode<number>,
left = 0,
right = trees.length - 1
) {
if (!trees.length) {
trees.push(tree);
return;
}
if (tree.key === trees[left].key) {
trees.splice(left + 1, 0, tree);
return;
}
if (tree.key === trees[right].key) {
trees.splice(right + 1, 0, tree);
return;
}
if (tree.key! < trees[left].key!) {
trees.splice(left, 0, tree);
return;
}
if (tree.key! > trees[right].key!) {
trees.splice(right + 1, 0, tree);
return;
}
let middle = (left + right) >> 1;
if (tree.key === trees[middle].key) {
trees.splice(middle + 1, 0, tree);
return;
}
if (tree.key! > trees[middle].key!) {
return binaryInsert(trees, tree, middle + 1, right - 1);
}
return binaryInsert(trees, tree, left + 1, middle - 1);
}
}
文件压缩原理
为了简单期间我们不考虑中文,只考虑ASCI码,即8bit表示一个字符,那么 一个文件的大小由字符数决定, 那么如何能减少文件大小呢?
一个简单的方案是允许<=8bit表示一个字符(可变长编码),经过一种编码转换后的字符数小于原字符数,从而达到压缩文件的效果。
可变长编码还要满足前缀编码要求,即不能出现两个相同前缀的的字符,这样解码时字符识别就不会有冲突,赫夫曼编码正好满足前缀编码的要求。
Huffman编码
- huffman编码是一种编码方式,属于一种程序算法
- huffman编码是Huffman树在电讯通信中的经典应用之一
- 它广泛用于数据文件压缩。其压缩率通常在20%-90%之间
- 它是可变字长编码(VCL)的一种。
为什么Huffman编码满足前缀编码要求
- 在Huffman树中规定向左的路径为0,向右的路径为1
- 只有叶子节点才参与编码,由于使用频繁的字符放在与根节点较近的叶子上,即使用的编码较短,这就实现了文件压缩的效果。
- 因为非叶子节点不表示字符,所以对叶子节点的编码就没有公共前缀问题,即满足前缀编码
文件压缩具体如何实现呢?
- 将字符串转换为字符数组
- 计算每一个字符出现的频次(这个频次就是Huffman树中的节点权重),生成
字符=》权重和权重=》字符的map映射,。 - 从小到大排序权重,生成
HuffmanTree - 再次读取字符数组,根据
HuffmanTree生成新的字符数组(要短很多) - 将新字符数组和
HuffmanTree写入文件,完成压缩
解压缩
- 读取
HuffmanTree,读取bit流,根据HuffmanTree的路径和char得到原字符,写入到文件中, 完成解压。
完整实现过程可以看这个视频
注意
- 一些格式的文件如
.ppt、.webp本身已经进行了压缩,再次使用霍夫曼编码压缩基本没有效果 - 一些文本格式文件如
.xml、.txt压缩效果会比较明显,尤其对重复内容比较多的文件来说。
B树
多叉树
二叉树查找效率较高,如果二叉树的节点少,没有什么问题。由于二叉树需要加载到内存,节点比较多,就存在如下问题

- 构建二叉树时需要多次进行IO操作(海量的数据存在数据库或文件中),节点海量,构建二叉树时,速度有影响
- 节点很多,会造成二叉树高度很大,会降低操作速度
如果我们允许每个节点可以有更多数据项和更多子节点,就可以降低树的高度和IO操作, 这就是多叉树。
举例来说2-3树就是一个多叉树

- 每个节点最多存放两个元素
- 每个节点最多有三个子节点
B树
B是balance,平衡的意思,2-3树 2-3-4树也是B树。
B树通过重新组织节点,降低树的高度,并减少IO读写次数来提升效率

-
文件系统及数据库系统的设计者利用磁盘预读原理,将一个节点的大小设为等于一个页(4K),这样每个节点只需要一次IO就可以完全载入
-
将树的度设置为1024,在600亿个元素中,最多只需要4次IO操作就可以读取想要的元素,B树广泛应用于文件存储系统及数据库系统中
- 树的度: 指其中节点的度最大值
- 节点的度: 节点的子节点数量
-
B树的阶: 节点的最多子节点个数叫做阶。比如2-3树的阶就是3,2-3-4树的阶就是4;
-
B树的搜索:从根节点开始,对节点内的元素进行二分查找,如果找到就结束,否则进入查找元素所属范围的子节点再进行二分查找,直到找到或者到达叶子节点;
-
B树的所有节点都会存放数据;
除了B树外,还有B+树和B*树
- B+树是B树的变种,只有叶子节点才存储数据,叶子节点是链表结构,链表中的数据也是有序的
- 非叶子节点中存放的是索引,而不是要操作的数据,每个非叶子节点都会存放叶子节点的索引,也叫稀疏索引;
- B+树一般用于文件系统;
- B*树又是B+树的变体,就是在B+树的基础上,在非根非叶子节点之间增加了指向兄弟节点的指针。
在B树中比较核心的是2-3树
2-3树的特点
- 所有的叶子节点都在同一层(B树的特征)
- 每个节点最多储存两个元素,每个元素最多3个节点
- 有两个子节点的节点叫做二节点,二节点要么没有子节点,要么只有两个子节点
- 有三个子节点的节点叫做三节点,三节点要么没有子节点,要么有三个子节点。
- 2-3树由二节点和三节点构成的树
以数列{16,24,12,32,14,26,34,10,8,28,38,20}构建2-3树的过程

本来打算自己实现一下2-3树,但是分析过来发现状态很多需要维护parent、left、right、center、vals 等很多状态,一时半伙搞不定,但最主要的原因是这些工作都是体力活,没有特别的难点,所以暂且不尝试实现了。
树的用途
- 比特币的交易树
MerkleTree - 以太坊的状态树
MPT(Merkle Patricia Tree) - MySql 索引的实现 B树的应用
- DOM, AST 等应用都是对人脑分层分类认知的建模, 都是树
- 文件压缩算法 (霍夫曼树)
堆
堆是一种完全二叉树, 堆也叫二叉堆。
二叉堆是计算机数据结构中非常著名的数据结构, 它能高效快速的找到最大值和最小值,常被用于优先队列。它也被用于著名的堆排序算法中。
二叉堆的两个特性
- 完全二叉树
- 不是最小堆就是最大堆
堆的应用
图
图的分类
- 有向图
- 无向图
图的表示法
- 邻接矩阵
- 缺点 比较耗费空间,删除节点很麻烦
- 优点 逻辑严谨,可以表示有向图
- 邻接表 邻接矩阵的改进,节省空间
- 关联矩阵 适用于边比顶点多的场景 (也比较耗费空间)
图的示例代码
tsexport class Graph<T = any> {
private vertices = new Set<T>(); // 顶点
private adjList = new Map<T, Set<T>>(); // 邻接表
constructor(public isDirected = false) {}
addVertices(v: T) {
if (!this.vertices.has(v)) {
this.vertices.add(v);
this.adjList.set(v, new Set<T>());
}
}
addEdge(v: T, w: T) {
this.vertices.add(v);
this.vertices.add(w);
let u = this.adjList.get(v);
if (!u) {
u = new Set<T>();
this.adjList.set(v, u);
}
u.add(w);
if (!this.isDirected) {
let u2 = this.adjList.get(w);
if (!u2) {
u2 = new Set<T>();
this.adjList.set(w, u2);
}
u2.add(v);
}
}
getVertices() {
return this.vertices;
}
getAdjList() {
return this.adjList;
}
toString() {
let s = '';
this.vertices.forEach((v, i) => {
s += `${v} -> `;
this.adjList.get(v)!.forEach((w) => {
s += w;
});
s += `\n`;
});
return s.length ? s.substring(0, s.length - 1) : s;
}
}
图的遍历方法
- 广度优先 队列
- 深度优先 递归+栈
tsimport { Queue } from './queue';
import { Stack } from './Stack';
export function breadthFirstSearch<T extends string = any>(
graph: Graph<T>,
startVertex: T,
callback: Function
) {
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
const queue = new Queue<T>();
const colors = [...vertices].reduce(
(sum, it) => {
sum[it] = Colors.WHITE;
return sum;
},
{} as { [key: string]: Colors }
);
queue.enqueue(startVertex);
colors[startVertex] = Colors.GREY;
callback(startVertex);
while (queue.size) {
const it = queue.dequeue()!;
colors[it] = Colors.BLACK;
const u = adjList.get(it)!;
u.forEach((_it) => {
if (colors[_it] === Colors.WHITE) {
queue.enqueue(_it);
colors[_it] = Colors.GREY;
callback(_it);
}
});
}
}
export function depthFirstSearch<T = any>(
graph: Graph,
v: T,
callback: Function
) {
const stack = new Stack<T>();
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
const colors = [...vertices].reduce(
(sum, it) => {
sum[it] = Colors.WHITE;
return sum;
},
{} as { [key: string]: Colors }
);
dfs(v);
function dfs(it: T) {
colors[it] = Colors.GREY;
stack.push(it);
callback(it);
const u = adjList.get(it)!;
u.forEach((it) => {
if (colors[it] === Colors.WHITE) {
dfs(it);
}
});
stack.pop();
}
}
图的算法
最短路径问题
- BFS广度优先算法 标记回溯点, 标记节点访问状态(未访问、已访问,已完全访问)
- dijkstra
- floyd
迪杰斯拉特算法
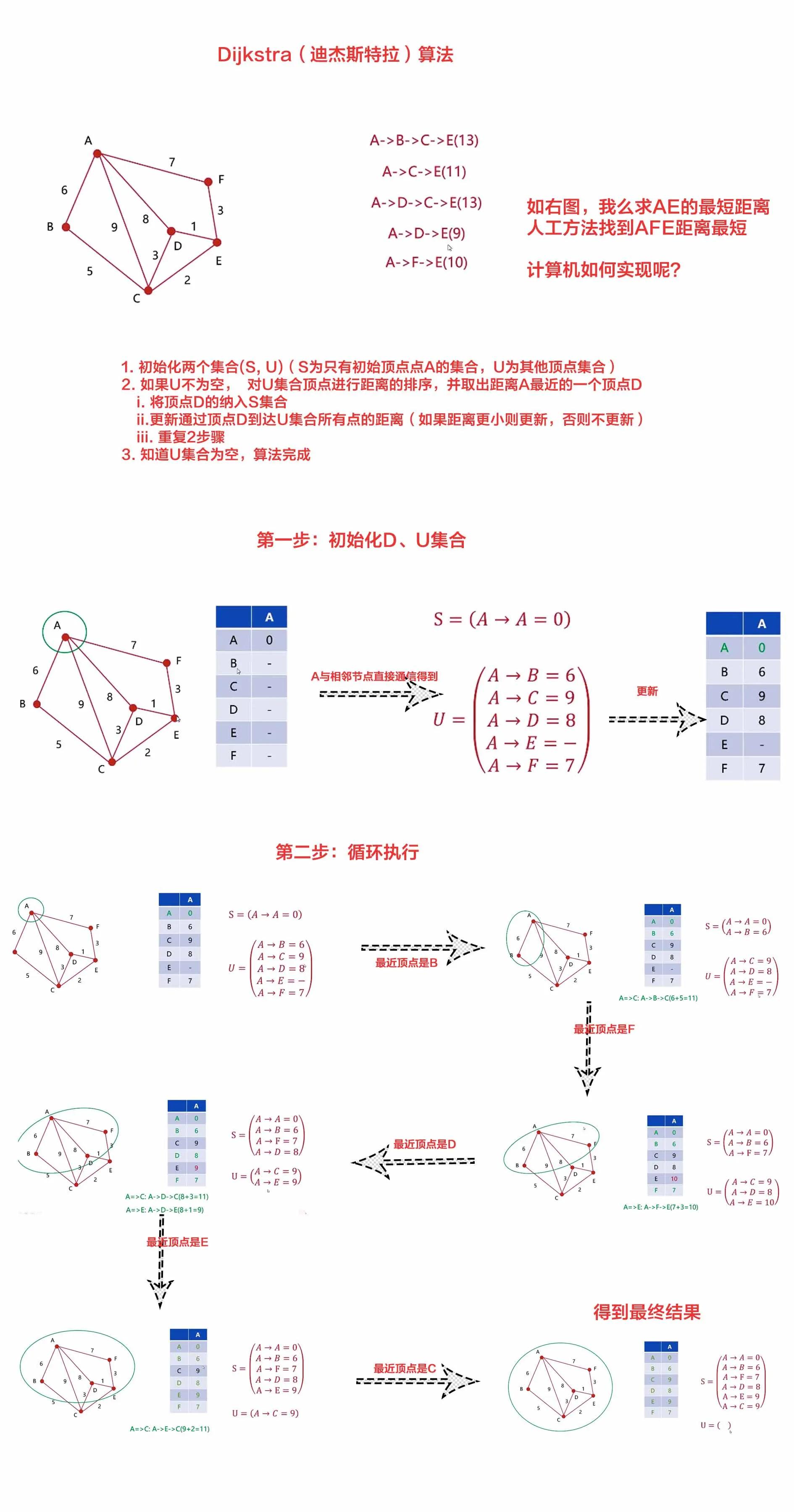
tsexport function dijkstra(graph: number[][], point: number) {
// 记录从point到其他点的距离
// s是已完成计算的点, u时未完成计算的点
// 0表示未知距离
const s = new Set<[number, number]>();
const u = new Set<[number, number]>();
s.add([0, graph[point][0]]);
graph[point].slice(1).forEach((it, index) => {
u.add([index + 1, it]);
});
const visited = {} as { [key: number]: boolean };
visited[0] = true;
while (u.size) {
let minIndex = 0;
let minDistance = graph[point][minIndex] || Number.MAX_VALUE;
[...u].forEach(([i, dis]) => {
if (!visited[i] && dis && minDistance > dis) {
minIndex = i;
minDistance = dis;
}
});
graph[point].forEach((it, index) => {
if (!visited[index] && it && minDistance > it) {
minIndex = index;
minDistance = it;
}
});
s.add([minIndex, minDistance]);
visited[minIndex] = true;
u.forEach((it) => {
if (it[0] === minIndex) {
u.delete(it);
}
});
// 比较 point --> i 与 point --> minIndex --> i之间的距离
u.forEach((it) => {
const [i, distances] = it;
if (graph[point][minIndex] && graph[minIndex][i]) {
const newDistance = graph[point][minIndex] + graph[minIndex][i];
if (distances === 0) {
it[1] = newDistance;
// graph[point][i] = newDistance;
} else if (distances > newDistance) {
it[1] = newDistance;
// graph[point][i] = newDistance;
}
}
});
}
return [...s].reduce((sum, it) => {
const [index, dis] = it;
sum[index] = dis;
return sum;
}, [] as number[]);
}
Floyd算法
ts/**
* Flody算法:求出每一对顶点之间的最短路径
* 使用动态规划思想,将问题的求解分成多个阶段
* 对于n个顶点的图G,求任意一对顶点Vi -> Vj之间的最短路径可分为如下几个阶段:
* #初始:不允许在其他顶点中转,最短路径是?
* #0: 若允许在V0中转,最短路径是?
* #1: 若允许在V0、V1中转,最短路径是?
* 。。。。。。
* #n-1: 若允许在V0、V1、。。。、Vn-1中转,最短路径是?
*/
export function floyed(graph: number[][]) {
// graph[i][j] 记录 i到j 的最短距离
// path[i][j] = x 记录从 i-->j 需要 x 中转
const path = Array.from(
{
length: graph.length,
},
() =>
Array.from(
{
length: graph[0].length,
},
() => -1
)
);
// 需要使用 0 - i个顶点进行中转
for (let k = 0; k < graph.length; k++) {
// 遍历所有顶点之间的距离
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < graph.length; j++) {
if (i === j) continue;
if (k === j || k === i) continue;
if (graph[i][k] === Infinity || graph[k][j] === Infinity) {
continue;
}
const newDistance = graph[i][k] + graph[k][j];
if (graph[i][j] > newDistance) {
graph[i][j] = newDistance;
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
return {
graph,
path,
};
}
最短路径算法总结

有权图的最短路径还有一种算法 DV矢量算法
最小生成树
图与树的区别
树其实是一种特殊的图,只有具备以下三个特点的图才是树
- 图必须是连通的
- 图必须是无环的
- 图必须是无项的
如果一个颗树有N个定点,那么它有且只有N-1条边,多一条边就会包含环结构,少一条边就没有连通所有顶点。
生成树
- 保留所有(N个)节点,保留(N-1)个边
- 保留的图是连通的,且没有回路
如果子图满足以上两个性质就是生成树
最小生成树
给定一个图,不一定只有一个生成树,在所有的生成树当中最小权重之和的那个树,才是最小生成树

最小生成树有什么用呢? 比如有一个村庄想铺水泥树,要求每两家之间必须有一条水泥路,且铺设的总费用最低。

这就是最小生成树要解决的问题
最小生成树的算法
- Prim算法
- Kruskal算法
Prim算法
以前面的图结构为例
- 用集合U记录生成树的节点, 随便选择一个节点,假设是v1
- 将
v1标记为红色,寻找与所有蓝色节点连接的最短边 v1-v4最短,选择v4,将其染成红色,继续寻找红色节点与蓝色节点的最短连线。v1-v2最短,循环执行步骤三直至将所有节点染成红色,这里依次选择的是v4-v3、v4-v7、v7-v6、v7-v5,这些节点与连线组成的图就是最小生成树。

算法实现
tsexport function prim(graph: number[][]) {
const visited: boolean[] = []; // 已经选择的顶点
const result: {
edge: [number, number];
weight: number;
}[] = [];
const { length } = graph;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
visited[0] = true;
for (let i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
const [s, u] = minEdge(graph, visited);
visited[u] = true;
visited[s] = true;
result.push({
edge: [s, u],
weight: graph[s][u],
});
}
return result;
function minEdge(graph: number[][], visited: boolean[]) {
// vertices1 已访问的顶点 未访问的顶点
const [vertices1, vertices2] = visited.reduce(
(sum, it, key) => {
it ? sum[0].push(key) : sum[1].push(key);
return sum;
},
[[], []] as [number[], number[]]
);
let s = 0,
u = 0,
minDistance = Infinity;
for (let i = 0; i < vertices1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < vertices2.length; j++) {
const newDistance = graph[vertices1[i]][vertices2[j]];
if (newDistance && newDistance < minDistance) {
minDistance = newDistance;
s = i;
u = j;
}
}
}
if (vertices1[s] > vertices2[u]) {
return [vertices2[u], vertices1[s]];
} else {
return [vertices1[s], vertices2[u]];
}
}
}
Kruskal算法
还是以前面的图为例子

- 创建一个队列 记录所有的边和权重, 这个队列按照权重从小到大排列
- 假设只有顶点没有边,每个顶点当成一棵树
- 从队列中取出一条边,如果连接的两个顶点不在一棵树上,则合并两颗树
- 如果取出的边在同一棵树则丢弃这条边,继续从队列中取出一条边
- 如果边的数量等于顶点数量减1,说明找到最小生成树树了,返回并终止程序。

代码实现
tsexport function kruskal(graph: number[][]) {
type Item = {
edge: [number, number];
weight: number;
};
const bst = new BinarySearchTree<Item>((a: Item, b: Item) => {
if (a.weight !== b.weight) {
return a.weight - b.weight;
}
if (a.edge[0] !== b.edge[0]) {
return a.edge[0] - b.edge[0];
}
return a.edge[1] - b.edge[1];
});
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < graph.length; j++) {
const weight = graph[i][j];
if (![0, Infinity].includes(weight)) {
bst.insert({
edge: [i, j],
weight,
});
}
}
}
const queue = new Queue<Item>();
bst.inOrderTraverse((it: Item) => {
queue.enqueue(it);
});
const treesVertices: number[][] = [];
const result: {
edge: [number, number];
weight: number;
}[] = [];
// 顶点 与 树(treesVertices的索引) 的映射关系
const map = Array.from({ length: graph.length }, () => -1);
enum State {
ONE_TREE,
TWO_TREE,
ONE_OTHER,
OTHER,
}
while (result.length < graph.length - 1) {
const { edge, weight } = queue.dequeue()!;
const state = check(edge);
// 0 表示两个顶点在已有的同一个树上
// 1 两个顶点在已有的不同的树上
// 2 一个顶点在已有的树上
// 3 两个顶点均不在一有的树上
if (state === State.ONE_TREE) {
continue;
}
result.push({
edge,
weight,
});
switch (state) {
case State.TWO_TREE: // 合并两个树
let treeIndex = map[edge[0]];
let treeIndex2 = map[edge[1]];
if (map[edge[0]] > map[edge[1]]) {
treeIndex = map[edge[1]];
treeIndex2 = map[edge[0]];
}
treesVertices[treeIndex2].forEach((v) => {
map[v] = treeIndex;
treesVertices[treeIndex].push(v);
});
treesVertices.splice(treeIndex2, 1);
break;
case State.ONE_OTHER: // 这棵树加入新顶点
if (map[edge[0]] === -1) {
map[edge[0]] = map[edge[1]];
treesVertices[map[edge[1]]].push(edge[0]);
} else {
map[edge[1]] = map[edge[0]];
treesVertices[map[edge[0]]].push(edge[1]);
}
break;
case State.OTHER: // 新生成一棵树并加入
const treeVertices = edge.slice();
map[edge[0]] = treesVertices.length;
map[edge[1]] = treesVertices.length;
treesVertices.push(treeVertices);
break;
}
}
return result;
function check(edge: [number, number]): State {
const [a, b] = edge;
if (map[a] === -1 || map[b] === -1) {
if (map[a] === map[b]) {
return State.OTHER;
} else {
return State.ONE_OTHER;
}
}
if (map[a] === map[b]) {
return State.ONE_TREE;
} else {
return State.TWO_TREE;
}
}
}
本文作者:郭郭同学
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
