目录
。。。。。。
被动语态
- 主动语态 强调动作的执行者
- 被动语态 强调动作的承受着
主谓宾
- The carrot was eaten by rabbit
- The rabbit was frightened by wolf
主谓+间接宾语+直接宾语
- The rabbit gave the carrot to the wolf
- The wolf was given the carrot by the rabbit
- The carrot was given to the wolf by the rabbit
主语+谓语+宾语+宾补
- The rabbit was invited to the party by the wolf
- The rabbit made the wolf (to) laugh
- The wolf was made to laugh (by the rabbit)
| 主动 | 被动 | 被动疑问 |
|---|---|---|
| The rabbit has eaten the carrot | The carrot has been eaten by the rabbit | Has the carrot been eaten by the rabbit |
| The rabbit would have eaten the carrot | The carrot would have been eaten by the rabbit | Would the carrot have been eaten by the rabbit |
| The rabbit might eat the carrot | The carrot minght be eaten by the rabbit | Might the carrot be eaten by the rabbit |
倒装句
为了强调某种信息 而颠倒原有语序的顺序
倒装分三种
- 完全倒装 谓语动词完全在主语前
- 副词/介词短语在句首的倒装
- 表语的倒装
- 部分倒装 仅助动词提前
- 形式倒装 谓语动词不提前
地点副词在句首的倒装
- There goes the last bus
时间副词在句首的倒装
- Now comes the wolf's turn!
表运动方向的副词在句首的倒装
- In out up down away
- Up went the carrot into air
- At the table sat a rabbit
英语中为了保持句子平衡,或者强调表语部分,将做表语的形容词、分词、介词短语、such, 置于句首时,需要完全倒装
- Seated on the ground is a group of rabbits
- Such were the wolf's tricks
- English you mush learn
- This video you like
部分倒桩句(将助动词和谓语动词分离,助动词提前)
- Never before have I eaten such a delicious carrot
独立主格结构
- Because he was invited by the wolf, the rabbit deside to go to party
Invited by the wolf, The rabbit deside to go to the party- Because the wolf invited him, the rabbit deside to go to the party
- The wolf Inviting him, the rabbit decided to go to the party
- 这句话的主干是
the rabbit ...,但是invite这个动作是由the wolf发出的,而不是真正的主语 the rabbit 发出来的,所以语法上把the wolf称为动词invite的逻辑主语,而这就是"独立主格"中的"主格",因为the wolf是有利于真正主语the rabbit之外的呀,所以是独立,这个独立的主语(非真正的主语)叫逻辑主语
- 这句话的主干是
下面看一下独立主格对句子的简化
| 标题 | |
|---|---|
| If the weather permits, the rabbit will go out | The weather permitting, the rabbit will go out |
| After the work was finished, the rabbit went home | The work finished, the rabbit went home |
| The rabbit is lying in the bed and a carrot is still held in his hand | The rabbit is lying in the bed, a carrot still held in his hand |

- The rabbit to come, the wolf is overjoyed
- Many animals went to the party, some of them rabbits and wolves
- Many animals went to the party, some of them happy
- The rabbit sat on a chair, head down
- The rabbit came in, carrot in hand
名词/代词 + being + ...
-
Many animals went to the party, some of them
beingrabbits and wolves -
Many animals went to the party, some of them
beinghappy -
The rabbit sat on a chair, head
beingdown -
The rabbit came in, carrot
beingin hand -
The work finished, the rabbit went home
-
With the work finished, the rabbit went home
-
The rabbit came in, with a carrot in his hand
- The rabbit came in, carrot in hand
强调
- Rabbits like carrots
- Wow rabbits like carrots!
- Oh my god, rabbits like carrots
书面强调
- Rabbits like carrots!
- Rabbits like carrots!!!
- Rabbits like carrot!?
- Rabbits like carrots
- RABBITS like carrots
词汇强调
-
Rabbit really like carrots!
-
I eat very very very fast!
-
I missed the very beginning of the movie
-
This is just unbelieveable!
-
All I ever wanted is that carrot
-
What the hell are you talking about
-
He went on and on and on
-
He walked and walked and walked
Rabbits do like carrots
反身代词强调
-
I can do it myself
-
I myself went there!
-
I saw myself in the mirror 这个不是强调
-
The carrot is big! ---> How big the carrot is !
-
You've grown a big carrot ---> What a big carrot you've grown!
-
The rabbit will eat the carrot
- It is the rabbit who/that will eat the carrot

省略
- 词法省略
- 句法省略
词法省略
表示独一无二的身份,可以省略冠词
chairman president head
- The rabbit was appointed (the) chairman of the carrotown Committee
- The wolf served as (the) head of our team
并列关系
- Both the rabbit and (the) wolf will be invited to the party
- Is this hunny a boy or (a) girl
有些情况下不能省略冠词
- a teacher and a wideo creator
某些独立主格结构可省略
-
The rabbit came in, carrot in hand
-
The rabbit came in, with a carrot in his hand
-
I ate 10 carrots (on) that day
-
I worked (for) 60 hours (in) last week
I am busy (in) making videos
裸不定式
- He wanted to stay here and (to) read
- The wolf helped me to eat the carrot
省略从句引导词
- This is the rabbit (that) we met yesterday.
- The rabbit said (that) the carrots were tasty
句法省略
祈使句
- Open the door please
- You open the door, please
- What a smart rabbit he is!
- How (fast) time flies!
在一些口语表达中力求简洁,可省略很多重复的部分
- The rabbit went home after work, and (the rabbit) ate a carrot
- The rabbit has eaten a carrot, but the wolf hasn't (eaten a carrot)
- The story made the rabbit happy, but (the story made) the wolf sad
- The rabbit likes carrots and the wolf (likes) apples
主从复合句中的省略
- The rabbit will eat the carrot , but I don't know when (he will eat it)
- When (the rabbit was) young, (he) went to school erery day
- If (it is) possible, I'll be there on time
- I can eat more carrots than you (can eat carrtos)
- You are smarter than I am smart
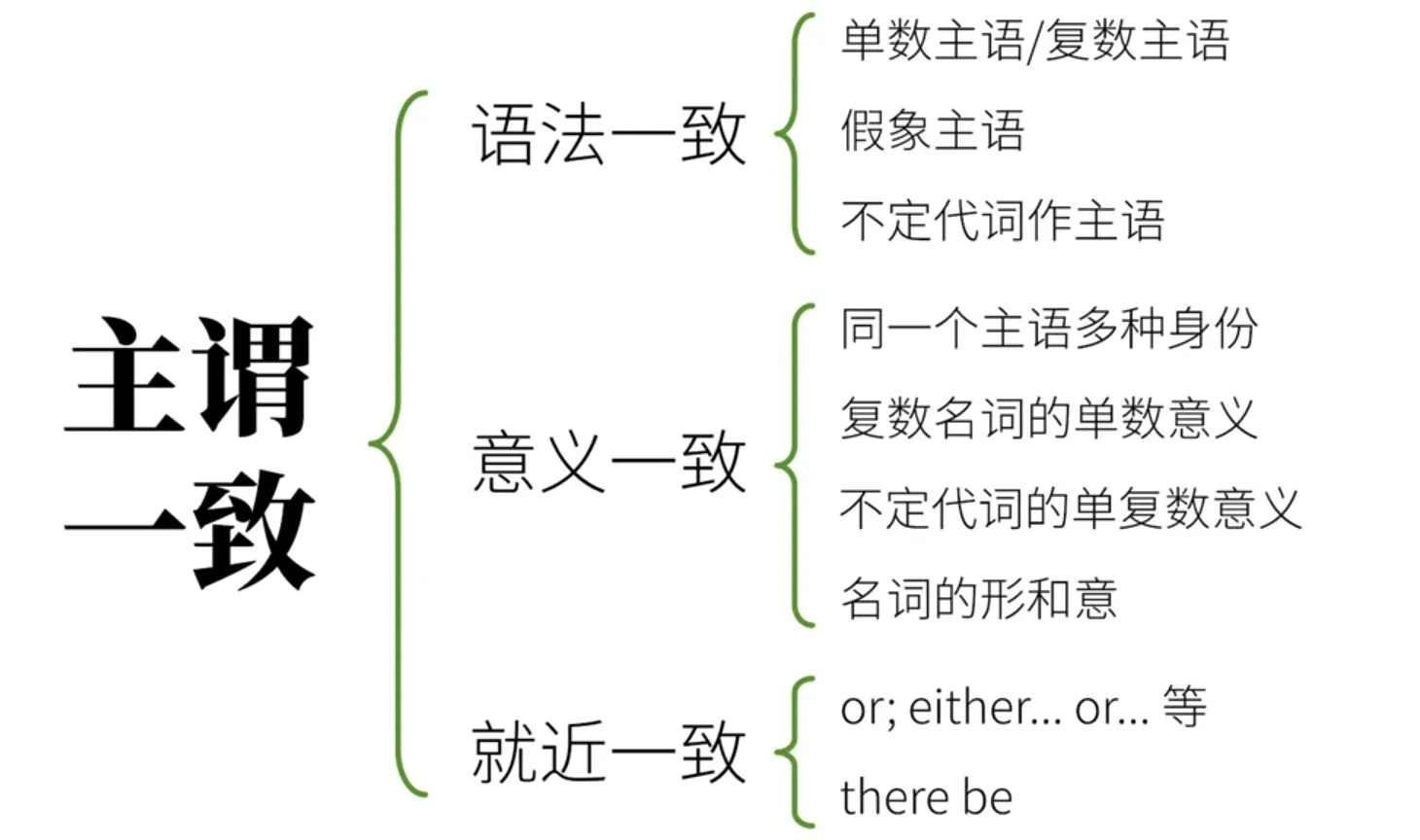
主谓一致
中文是所谓孤立语,对次序的要求非常高,而词性变化很少或者没有变化。 比如咱们中文没有动词本身不存在于语法上的“变位”,(时态气)
而英文术语屈折语,通过丰富的词性变化表达语法意义。
如 I am a rabbit, you were a rabbit
谓语动词和主语的人称一致,
英语语法 主谓一致,要求 语法一致、意义一致、就近一致
语法一致
句子中的谓语动词在形式上和主语的单复数保持一致
- Time is money
- Carrots are delicious
不可数名词后只能接单数谓语动词
比如
- A number of carrots have been eaten
- A lot of carrot juice has been sold
- To eat a carrot every day is good for the rabbit
非谓语动词做主语时,也相当于单数名词, 比如
- To eat a carrot every day is good for the rabbit
- Eating carrots is healthy
一般情况下用and连接不同的名词做主语,都会接复数谓语动词,比如:
- The rabbit and the wolf are at the party
假象主语 一些词看起来像复数,但其实是单数
-
as well asexpectbut -
The rabbitas well as other animalsgetsa rabbit -
All the animalsexcept the wolfgetthe carrots
不定代词作主语
-
Everyone gets a carrot
-
Each of them gets a carrot
-
Both of them like carrots
-
Some of them are afraid of wolf
-
None of them get/gets a carrot
-
Neigher of them is/are afraid of the wolf
意义一致
主语意义位单数, 则谓语动词用单数, 主语意义为复数, 则谓语动词也需要用复数
同一个主语多种身份
- The teacher and video creator is a rabbit
- The teacher and the video creator are rabbits
意义一致
- Ten years is a long time
- Two coins isn't a lot
- A knift and fork is needed for eating the carrot
- Break and butter is also needed at dinner
- 不定代词的单复数意义
- All is quiet --> All are quiet
- 名词的行和意
- 行复意单 ---> 用单数谓语动词
- 行单意复 ---> 用复数谓语动词
- 单复数同形的名词 ---> 用单复数谓语动词都可
- 集合名词 ---> 用单复数谓语动词都可
有些名词,看起来是单数, 但是意义是单数, 比如:
- Physics is my favorite subject
- The cattle are on the hill
- A sheep is eating grass
- The sheep are eating grass
类似的名词还有 deer means series species
集合名词
- The rabbit's family is huge.
- The rabbit's family are all at home
类似的集合名词还有
- army audience police team police team 等
只能表示一个类别的事物, 只能用单复数谓语动词如
- All the funiture here is expensive
the + 形容词
可视作集合名词;表示单数意义/复数意义
- The young are expected to learn from the old
- The new is going to replace the old
就近一致
谓语动词的单复数由最近的主语决定,如or,either... or... 等
由 or... / either... or... / neither...nor.../ not only... but alse 等连接两个名词或代词作主语时, 谓语动词和和离的近的词一致
- Either you or I am going to party.
- Not only the rabbit but also many other animals like carrots
- There is a carrot and two apples on the table
缩写
| contraction | example sentence |
|---|---|
| I am ---> I'm | I'm 24 years old |
| You are ---> You're | You're such a sweetheart |
| He is ---> He's | He's so handsome |
| She is ---> She's | She's very beautiful |
| They are ---> They're | They're such cute kittens |
| We are ---> We're | We're going to China next month |
| That is ---> That's | That's awesome |
| There is ---> There's | There's the hotel we were looking for |
| What is ---> What's | What's the matter? |
| Where is ---> Where's | Where's my car? |
| Who is ---> Who's | Who's there? |
| Who are ---> Who're | Who're the people at next table? |
| 12 | 12 |
| Are not ---> Aren't | They aren't coming next week |
| Is not ---> Isn't | She isn't listening to you |
| Were not ---> Weren't | They weren't invited to the party |
| Was not ---> Wasn't | I wasn't joking when I said that |
| Does not ---> Doesn't | He doesn't play tennis |
| Do not ---> Don't | I don't like cheese |
| Need not ---> Needn't | You needn't worry about that. |
| Did not ---> Didn't | I didn't know that |
| Can not ---> Can't | I can't understand you |
| Could not ---> Couldn't | He couldn't get his shoes on! |
| Will not ---> Won't | I won't be able to attend the conference |
| Would not ---> Wouldn't | I wouldn't ask her |
| Has not ---> Hasn't | She hasn't finished her homework yet |
| Have not ---> Haven't | I haven't finished my home work |
| Had not ---> Hadn't | I hadn't thought of that |
| Might not ---> Mightn't | I almost wondered if he mightn't be right |
| Must not ---> Mustn't | You mustn't worry too much about this |
| Should not ---> Shouldn't | You shouldn't do things like that |
| 18 | 18 |
| I will ---> I'll | I'll be on vacation next week |
| You will ---> You'll | I think you'll pass the exam |
| He will ---> he'll | I'm sure he'll help you if he can |
| She will ---> She'll | She'll be there tommorrow, I'm sure. |
| They will ---> They'll | I hope they'll come to my party |
| I would ---> I'd | I'd like a cup of coffee |
| You would ---> You'd | I was afraid you'd ask me that |
| He would ---> He'd | He'd lick to go to the cinema tonight |
| She would ---> She'd | She'd be a great managing director. don't you think? |
| They would ---> They'd | They'd love to see the film |
| We would ---> We'd | We'd be gratefull for an answer |
| 11 | 11 |
| I have ---> I've | I've been waiting an hour already |
| You have ---> You've | You've got to start working harder |
| They have ---> They've | They've got paint all over the carpet |
| We have ---> We've | It's been over a year since we're done that |
| Who have ---> Who've | Who've you asked so far? |
| He has ---> He's | He's worked here for 5 years |
| She has ---> She's | She's been to Japan twice |
| There has ---> There's | There's been entirely too much asid on the subject |
| That has ---> That's | That's got to be the most ridiculous thing I've ever seen |
| What has ---> What's | They want a list of what's been stolen |
| Who has ---> Who's | Who's been chosen, do you know? |
| I had ---> I'd | I'd just got in the bath when the phone rang |
| You had ---> You'd | It happened just after you'd left the room |
| He had ---> He'd | He'd been alone for a long time |
| She had ---> She'd | She'd already left |
| They had ---> They'd | They'd better be here on time |
| We had ---> We'd | We'd better be more careful in th fulture |
| Who had ---> Who'd | She wondered who'd sent her the mysterious email |
| 18 | 18 |
| Let us ---> Let's | Let's go out to dinner |
条件句
英语的条件句有时被称为“IF从句”, 分为真实条件句和非真实条件句,它描述了,可能发生(现在或将来)或可能发生但没有发生(过去)的事情的结果
由不同的时态组成,主要由四种条件句:
- 零条件句、
- 第一类条件句、
- 第二类条件句和
- 第三类条件句。
零条件句
格式: If/When + ...一般现在时...,
用法: 当结果总是发生时,或绝对真理时,使用零条件句
- If water reaches 100 degrees, it boils
- If people eat too much, they get fat
- If you touch a fire, you get burned
- Snakes bite if they scared
- if babies are hungry, they cry
- If the weather is nice, she walks to work
- I read if there is noting on TV
If 和 when
If 和 when都可以用于零条件句,但是 if表示某事发生频率较低, 而when表示有规律的发生,例如
- When I have a day off from work, I usually go to beach
第一类条件句
格式: If/When + ...一般现在时..., ...一般将来时...
用法: 当你用来描述你认为将来可能发生的事情时,使用第一类条件句。
- If it rains, I won't go to park
- If I study today, I'll go to the party tonight
- If I have enough money, I'll buy some new shoes
- She'll be late if the train is delayed
- If I see her, I'll tell her.
If 和 When If 表示你不知道某事是否发生,而when表示某件事一定会在某个时刻发生,我们只是在等待它的发生。
- When you call me, I will give you the address
第二类条件句
格式:
- If+...一般过去时...,...would + 不带to不定式...
- ...would + 不带to不定式...,If+...一般过去时...
用法
用来表示与将来事实可能相反的事情,比如在幻想什么东西
- If I won the lottery, I would buy a big house.
- She would pass the exam if she ever studied
- She would travel all over the world if she were rich
- If I had his number, I would call him
- 在第二类条件句中,虽然 was 经常出现在对话中,但是在语法上它是不正确的,在英语写作或考试中要用 were,例如:
- If he were French, he would live in Paris.
- I would play basketball if I were taller.
- if 和 when:只有 if 可以用于第二类条件句,而 when 不可以。
更多条件句,参考这篇文章
不定式省略to的情况
- 情态动词(除ought外)
- 使役动词 make, let, have 后,感官动词see, watch,look at, noice, abserve, hear, listento, smell, feel, find 等后。
- I saw him dance.
- The boss made them work the whole night.
- 注意被动语态中不能省去to. 例如:
- He was seen to dance
- The were made to work the whole night
- 实义动词get(说服。。。)后的to不能省略
- I'll get the wolf to wash my car for free
- would rather, had better句型后
- Why.../ Why no...句型后
- help sb (to) do sth
- The wolf helped the rabbit (to) grow carrots.
- but和except后。but前时实义动词do时,后面出现的不定式不带to.
- He wants to do nothing but go out
- He wants to believe anything but to take the medicine
- 由and, or和than连接的两个不定式,第二个to可以省去
- 通常在discover, imagine, suppose, think等词后作宾语时,可以省去to
其它
- 其它使役动词
- force(强迫),
- leave(让,导致),
- drive(驱使,使...变得),
- see(看到),
- find(发现)
- watch 观看
翻译问题

本文作者:郭郭同学
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!